A Polarizing Beamsplitter Cube is an optical component consisting of two right-angle triangular prisms combined, with a dielectric beamsplitter coating furnished at the one prism’s hypotenuse. The working principle of polarizing beamsplitter cubes is: when an unpolarized beam is incident on the polarizing beamsplitter cube, it is separated into two orthogonal polarizations: the s component and the p component. Due to the existence of the dielectric, polarization-sensitive coating, The s polarization will be blocked at the interfaces of the prisms, while the p polarization continues to propagate and emerges from the polarizing beamsplitter cube. The contrast of the transmission of component s and component p measured at the exit of the PBS cube is the extinction ratio Tp: Ts of the polarization beamsplitter cube.
Shalom EO offers Stocked and Custom High Power Polarizing Beamsplitter Cubes made from Corning C7980-0F and BK7. Regarding the standard products, prevalent laser line wavelengths are available: 355nm, 515nm, 535nm, 808nm, 1030nm, and 1064nm, whilst custom broadband versions between 700-900nm are also procurable. A multi-layer dielectric beamsplitter coating is positioned at the interface of the two prism parts, and the four faces where light enters and exits are anti-reflection coated to mitigate reflection loss, contributing to an extinction ratio of 1000:1, while other wavelengths, bandwidths, and extinction ratios (Max. 10000:1) could be tailored upon request. Shalom EO utilizes an adhesive-free, optical-contacted method to assemble the constituent prisms, the cubes are high-precision laser-grade polished to ensure minute wavefront distortion and allow optical contact, without the possibilities of degradation of cement, this implies a higher damage threshold and power limit of our products. Our PBS cubes feature an exceptional LIDT of >15J/cm2@1064nm, 20ns, 20Hz. Furthermore, the optical contact architecture is viable on the premise that the interfaces of the prisms are high-precision polished, so optical contact could reduce thermal absorption and minimize scattering loss simultaneously.
Application Notes:
1. About the angle of incidence, there are two common alternatives for polarizers made from glass materials: you either project the beam at 45° or at the Brewster angle. However, for polarizers made from crystals such as Glan laser polarizers, the incidence angle could be 0°, 45°, or the Brewster angle. This is because crystal polarizers function using birefringence, but the glass PBS cubes function using dielectric coatings.
2. It is worth noting that the operation of the polarizing beamsplitter cube is dependent on wavelength. Furthermore, in the aspect of polarization purity, polarization beamsplitter cubes are far less advantageous than crystal polarizers, for instance, Glan Thompson polarizers exhibit a much higher extinction ratio than PBS cubes.

Figure 1. Shows the working principle of polarizing beamsplitter cubes. First, the incident beam is divided into two orthogonal polarization components, the p component (which is marked in blue in the diagram), and the s component (which is marked in red). At the diagonal of the PBS cube where a polarization-sensitive beamsplitter dielectric coating is tiled, the s component is rejected, while the p component is allowed to exit.
Curves:
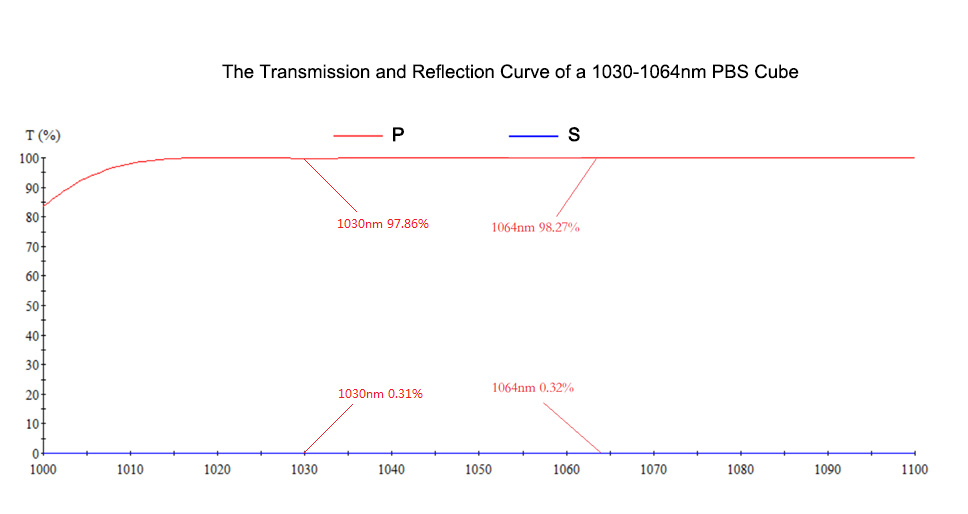
1. The Transmission and Reflection Curve of a 1030-1064nm PBS Cube
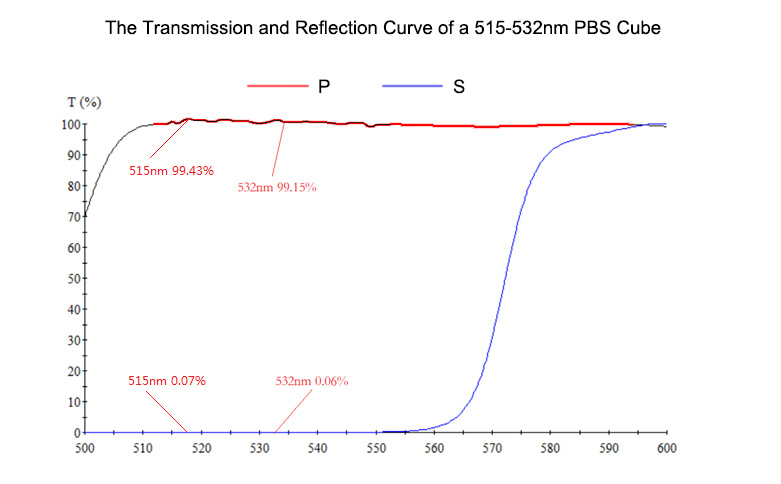
1. The Transmission and Reflection Curve of a 515-532nm PBS Cube