| Code | Material | Aperture | Side Length | Thickness | Surface Quality | Angular Tolerance | Flatness | Coating | Unit Price | Delivery | Cart |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1406-001 | F2 | >90% | 10mmx10mmx10mm | 10mm | 60/40 S/D | ±3 arc min | λ/10@633nm | Uncoated | Inquire | 4 Weeks | |
| 1406-002 | F2 | >90% | 15mmx15mmx15mm | 15mm | 60/40 S/D | ±3 arc min | λ/10@633nm | Uncoated | Inquire | 4 Weeks | |
| 1406-003 | CaF2 | >70% | 15mmx15mmx15mm | 15mm | 40/20 S/D | ±10 arc min | λ/2@633nm | Uncoated | Inquire | 4 Weeks | |
| 1406-004 | F2 | >90% | 20mmx20mmx20mm | 20mm | 60/40 S/D | ±3 arc min | λ/10@633nm | Uncoated | Inquire | 4 Weeks | |
| 1406-005 | F2 | >90% | 25mmx25mmx25mm | 25mm | 60/40 S/D | ±3 arc min | λ/10@633nm | Uncoated | Inquire | 4 Weeks | |
| 1406-006 | UV Fused Silica | >90% | 25mmx25mmx25mm | 25mm | 60/40 S/D | ±3 arc min | λ/10@633nm | Uncoated | Inquire | 4 Weeks | |
| 1406-007 | CaF2 | >90% | 25mmx25mmx25mm | 25mm | 60/40 S/D | ±3 arc min | λ/10@633nm | Uncoated | Inquire | 4 Weeks | |
| 1406-008 | CaF2 | 70% | 25mmx25mmx25mm | 25mm | 40/20 S/D | ±10 arc min | λ/2@633nm | Uncoated | Inquire | 4 Weeks |
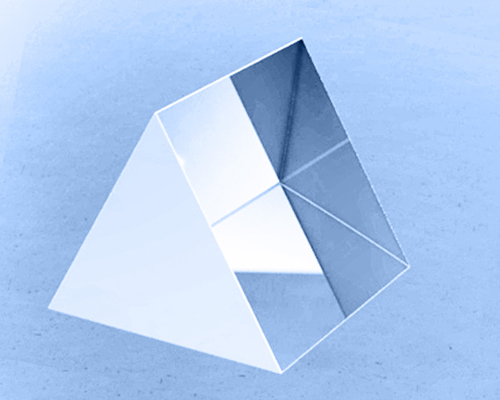
An Equilateral Prism is a triangular prism of three identical side lengths and 60°apex angles. Equilateral prisms are often utilized for dispersive purposes (i.e., separating a white light source into a spectrum of multiple colors). Depending on the substrate materials, equilateral dispersive prisms could be selected to break up different spectral regions. To some extent, equilateral prism functions just like a diffraction grating, only that the prisms present better brightness, greater endurance to power, and fewer problems associated with higher orders.
This page features Shalom EO’s Stocked Equilateral Prisms made of SCHOTT F2, CaF2, and UV Fused Silica.
F2 is a glass code from the German elite corporation SCHOTT. It is a flint glass with exceptional optical transmission between 0.37 to 2.3 micros. F2 Equilateral prisms work great for dispersion purposes due to their low abe number and high refraction. It also exhibits distinguished chemical inertia. (When a P-Polarized light is projected on the equilateral prism at the angle of minimum deviation, the reflection loss of this polarization will be small even without AR coating).
Calcium Fluoride (CaF2) is an excellent optical material with its high transmission between 180-8000 nm with low levels of fluorescence. CaF2 is often utilized in applications in the UV and IR spectra. CaF2 has a prominent LIDT (Laser-Induced Damage Threshold) value, a small refractive index, and low birefringence. Besides, Calcium Fluoride also exhibits higher mechanical hardness and more chemical stability than other fluoride counterparts, in addition to that CaF2 is not prone to deliquesce and enduring thermal shock.
UV Fused Silica is an excellent UV-transmitting optical glass material with a superior transmission rate to the UV wavelengths, meanwhile also being transparent to visible and NIR radiations (transmission range 200-2200 nm). The thermal properties of UVFS are remarkable, too, UV Fused Silica is durable to high-temperature and not susceptible to thermal expansion. Other virtues of UV-fused silica lenses encompass few bubbles/striae, high homogeneity, and advantages of birefringent properties.
With vanguard production techniques and rigorous inspection standards, our team is capable of manufacturing equilateral prisms of high precision, with a dimension tolerance of ±0.15mm, surface flatness of λ/10@632.8nm, and an angular tolerance of ±3 arc min. Under normal circumstances the off-the-shelf equilateral dispersive prisms are uncoated, but custom coatings could also be tailored. As a sophisticated supplier of optical components, besides the stocked equilateral prisms, we are also capable of providing custom equilateral prisms with a wide selection of substrate materials, coating options, and specifications.
Application Notes:
Equilateral dispersive prisms are often operated at the minimum angle of deviation. This angle is often obtained when the light path inside the equilateral prism is parallel to the bottom face of the equilateral prism, and the angle of the entrance is equal to the angle of emergence measured with respect to the normals at the respective interfaces. When the minimum angle of deviation is obtained, subsequent gains include maximum clear aperture, and reduction of reflection loss of p-polarization since the incident angle under this circumstance is now close to the Brewster’s angle.
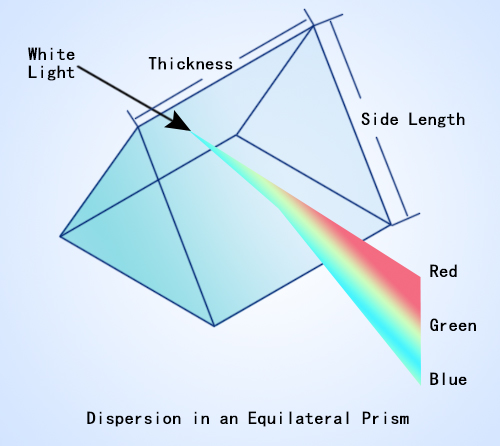
Figure 1. shows how a white light source incident on an equilateral prism is separated into multiple colors.
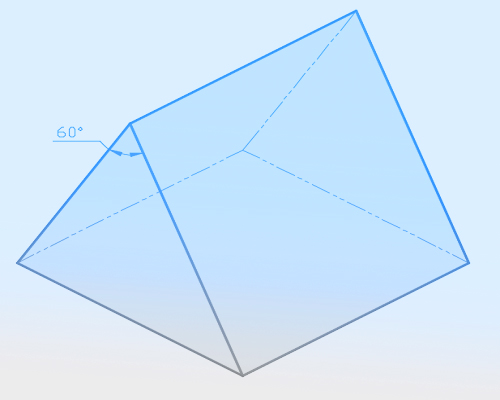
Figure 2. shows the internal structure and the outline of an equilateral dispersive prism.
Specifications:
| Material | F2, CaF2,UV Fused Silica | Clear Aperture | >90% |
| Dimension Tolerance | ±0.15mm at best | Surface Quality | 40/20 S/D or 60/40 S/D |
| Angular Tolerance | 3 arc min at best | Flatness | λ/10@632.8nm at best |
| Coating | Uncoated, or Custom | Bevelling | <0.2mmx45° |